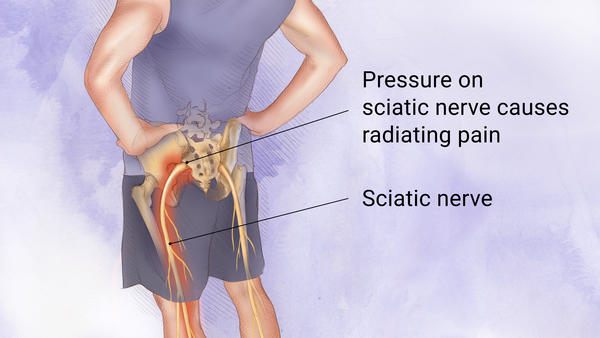
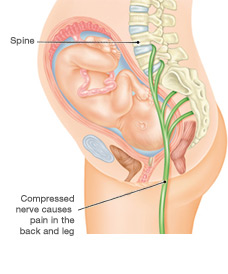
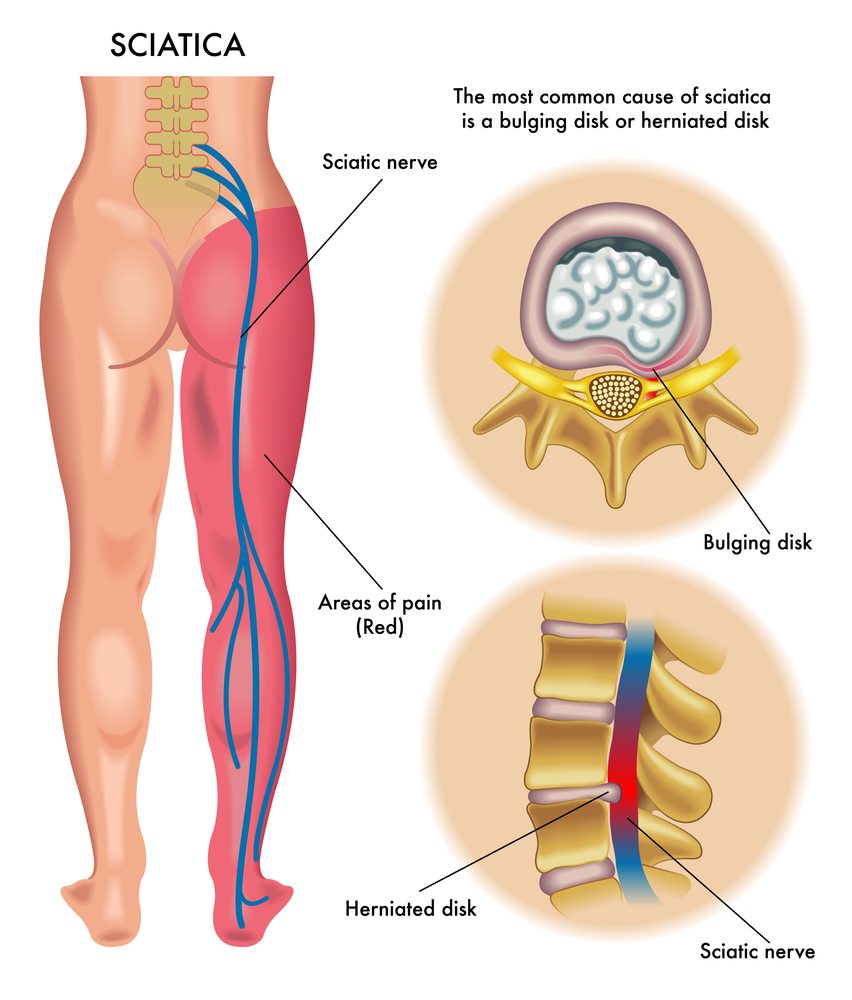
Sciatica
Does Gabapentin Help Sciatica

Among the many questions that people with sciatica have is: does gabapentin help sciatic pain? Does gabapentin give immediate pain relief? And how long does it take to start working? In this article, you will learn more about this medication. You will find out about its side effects, how it works, and whether it is right for your sciatica. You will also get some useful information about your treatment options.
What is Gabapentin?
In 2016, gabapentin was the 10th most commonly prescribed drug in the United States, with 64 million prescriptions written for it. However, the risks of gabapentin use are well known, and patients are encouraged not to use it past the expiration date on their prescriptions. Moreover, gabapentin isn’t a Schedule IV controlled drug, so it has lower risks for abuse than other drugs on the schedule. Its medical use is widely accepted in the U.S., including for analgesic, low back pain, antidiarrheal, and antitussive purposes.
Before taking gabapentin, it’s important to understand what the risks and side effects are as well as the frequency and severity of the pain. Because of the potential for interactions with other medications, gabapentin should be taken only with the advice of a physician. If the doctor only limits the dosage to twice daily, then you should only drink them twice. Also, gabapentin should never be used by pregnant women. It may increase the risk of the fetus having cardiac malformations or being too small for gestational age. Still, it may be an option for women with epilepsy to reduce seizure frequency.
Before starting this pharmacological treatment, patients should read the Patient Information Leaflet or Medication Guide. Generally, gabapentin is taken by mouth. The dosage depends on the medical condition, weight, and response to treatment. Half-tabs should be taken at the scheduled time, while capsules should be swallowed whole. Before beginning gabapentin, patients should consult a physician if they experience any side effects.
Patients should also make sure that they only take in the dosage recommended by their physician to avoid decreased pain control. Neuropathic pain brought on by sciatica can be difficult to manage. It is important to make sure that health and care excellence is exercised when dealing with severe burning pain or severe shooting pain.
Is Gabapentin Good for Sciatica?
The anticonvulsant drug Gabapentin is effective for reducing the pain of low back and nerve-related back pain. It is part of a class of drugs called gabapentinoids. It is most commonly used to treat neuropathic back pain, including spinal stenosis, which is a narrowing of the lower spinal canal that pinches nerves. It is also known to relieve symptoms of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. In addition to treating back pain, gabapentin also helps to increase the walking distance and reduce the severity of symptoms of sciatica.
In a 2016 randomized clinical trial, gabapentin was added to a regimen of amitriptyline to reduce the symptoms of sciatica. With the regimen, the patient’s pain improved rapidly. However, side effects were common, and patients reported a decreased improvement in their symptoms. This study highlighted that guidelines and research about the treatment of sciatica are contradictory and conflicting. Furthermore, topical products are not recommended by many clinical guidelines due to a lack of clinical evidence.
Adults with chronic central nervous system conditions need physical therapy and pharmacologic management to reduce pain. Potential option for treatment for lower back pain have long been part of the study medication for sciatica. But like many medical trials, data collection for secondary outcomes isn’t always available. This is why more research beyond primary outcomes should be done.
In a study comparing the two drugs for chronic sciatica, gabapentin was found to be better than pregabalin although both had only limited pain relief. In addition, gabapentin was associated with fewer adverse effects than pregabalin, and reduced leg pain severity more than pregabalin. However, it is recommended to start with gabapentin before starting pregabalin.
Does Gabapentin Give Immediate Pain Relief?
Although gabapentin gives immediate pain relief for sciatica, it is not without its risks. The drug may cause adverse effects, and at least half of the patients will not experience any worth while pain relief. This is why further studies are needed to determine whether gabapentin can provide effective treatment for sciatica. In the meantime, the drug may be a valuable adjunct to a rehabilitation program for neuropathic pain in adults.
Gabapentin is available in various forms, including extended-release tablets, capsules, and oral solutions. It is recommended to start with a low dosage and increase it gradually, to avoid possible side effects. It is also important to follow the dosage instructions carefully, and if you are unsure, call a pharmacist for advice. In the event that the dosage is too high, consult your physician.
Pharmacologic intervention is needed in pain management especially for sciatica. Treatment of sciatica study involves comparing pregabalin versus gabapentin. In the treatment of sciatica, it is important to know the difference between drugs and how they might interact with one another . When it comes to gabapentin vs pregabalin, more studies need to be conducted regarding its effectivity against disk herniation, sciatic nerve pain, neck pain and other spine pain.
Patients who were already taking amitriptyline were often prescribed gabapentin in addition to amitriptyline to treat sciatica or herniations disc. However, the drug was associated with severe adverse effects, and many patients reported reduced improvement in symptoms. Furthermore, the guidelines on sciatica treatment are conflicting, and topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatories aren’t mentioned in them. Moreover, there are no clinical studies that support their use.
How Long Does Gabapentin Take to Work?
Gabapentin is a prescription drug that is used for the management of neuropathic pain. It is available in capsules, tablets, and liquids. Gabapentin is usually prescribed at a low dosage and increased gradually to prevent side effects. The effective dosage ranges from three hundred to six hundred milligrams per day. However, the amount of gabapentin needed may vary depending on a person’s condition and health history.
In general, gabapentin will start working for nerve pain after about four weeks of treatment, although it may take longer for some people. It works by inhibiting certain chemicals in the body and affecting the nerves, which are the source of pain. As a result, gabapentin will reduce the pain and prevent it from returning. While gabapentin may not work for everyone, it is an effective treatment for chronic and severe pain.
It is important to know that withdrawal symptoms can occur after discontinuing gabapentin. It is important to discuss these symptoms with your doctor before stopping gabapentin. If you have any of these symptoms, contact your doctor as soon as possible. If you have any other concerns, discuss them with your doctor. As with any medication, gabapentin can have serious withdrawal symptoms and should not be stopped without medical supervision.
When is the Best Time to Take Gabapentin?
The best time to take gabapentin for sciatica depends on the severity of your pain and your individual circumstances. Generally, gabapentin is most effective when it is taken for at least 4 weeks. The treatment is not for treating aches and pains caused by arthritis or minor injuries. The World Health Organization does not study gabapentin use for longer than 5 months. However, if you have no other serious side effects and your healthcare team approves of your treatment plan, you can continue taking gabapentin for as long as you need to.
To ensure the best results from gabapentin treatment for patients with chronic sciatica, it is recommended that you take the first dose in the evening and the next at bedtime. However, the initial dose may take a few weeks to work. Your doctor may increase your dose slowly at first, and you can stop taking gabapentin if you experience significant relief from your symptoms. The best time to take gabapentin for sciatica is after your doctor has checked your condition and advised you to take the first dose at bedtime.
One recent study compared gabapentin with pregabalin to see if it would improve symptoms in people with chronic sciatica. Researchers found that gabapentin had fewer adverse effects than pregabalin and was associated with a greater reduction in leg pain intensity. Additionally, gabapentin was associated with fewer side effects, which is a bonus.
What Can You Do for Unbearable Sciatica?
Treatment for sciatica is generally self-care, and it can include alternating hot and cold packs. Icing your affected area for 20 minutes at a time for at least a couple of days can relieve pain and swelling. It can also help to keep moving and avoid lying on the affected area. Cold packs are most effective for relieving pain in the short term. A bag of frozen vegetables wrapped in a towel can also help.
If the pain persists, you should see a physician. If you are able to do so, write down your symptoms and any key medical information, including any recent injuries. You should also write down your questions for your doctor so that you can remember them later. Your family can also help you remember what your doctor told you, which can make the visit easier. Also, write down any additional information you would like your doctor to know, such as how much the pain has affected your quality of life.
If conservative treatments are not working, your doctor may recommend medication. There are several medications that are effective for sciatica pain, including stronger muscle relaxants and NSAIDs. Your doctor may also prescribe steroid injections three times a year, acupuncture (in which needles are inserted into specific points on the body), and spinal manipulation, which involves moving your spine to relieve pain.
Conclusion
A review of recent trials suggests that gabapentin may be effective for treating sciatica. However, the authors of the study note some limitations. For example, they found no statistically significant differences in composite outcomes, such as pain severity and duration, among the three groups of patients. Additionally, there was no statistically significant difference in the rate of surgery among patients in either group. Despite these limitations, the authors believe that gabapentin may be a reasonable option for those who are suffering from sciatica.
In a recent study, researchers evaluated the efficacy and safety of gabapentin for the treatment of acute sciatica in adults. They found that gabapentin was effective in treating sciatica and inhibiting central sensitization, which would make it an ideal treatment option for people with sciatica. However, further clinical trials are needed to confirm this finding. Therefore, gabapentin is currently a viable option for those suffering from acute sciatica.
In this study, researchers used a murine model to induce neuropathic pain in mice. The results of the study revealed that gabapentin was more effective than tramadol, which was used as a control for adverse events. Furthermore, gabapentin was found to be two-and-a-half times more effective than tramadol in reducing spinal inflammatory responses. These findings are consistent with previous reports.